Traversing Array From The Right
Find Last Occurrence of Target in Array
Description:
Given an integer array nums and an integer target, return the index of the last occurrence of target in nums. If the target is not found, return -1.
You must solve this problem with an efficient O(n) time solution by traversing the array from right to left.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
- -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
- -10^9 <= target <= 10^9
from typing import List
def find_last_occurrence(nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
"""
Returns the index of the last occurrence of target in nums.
If the target is not found, returns -1.
"""
# Traverse from rightmost index to left
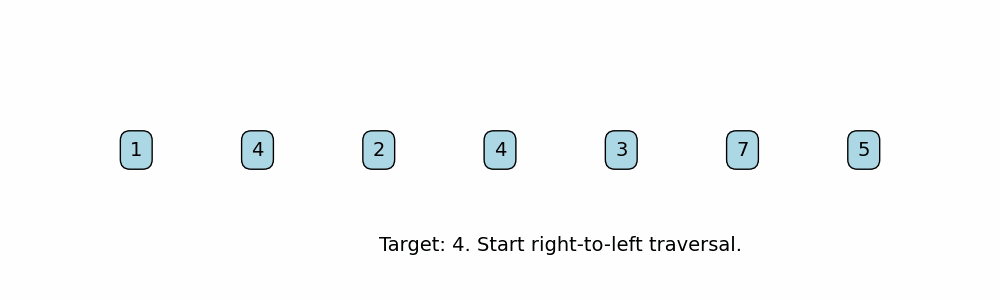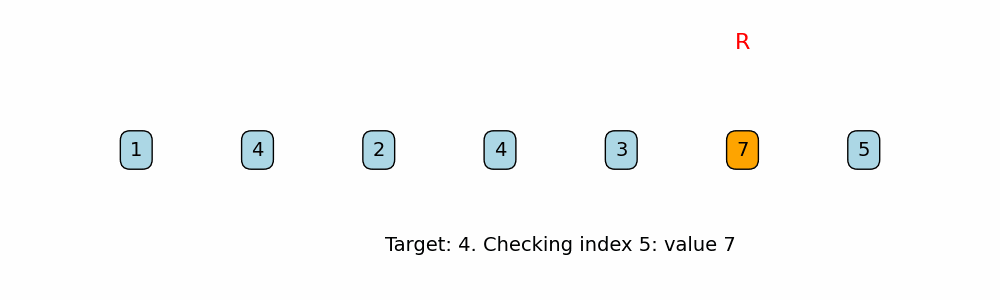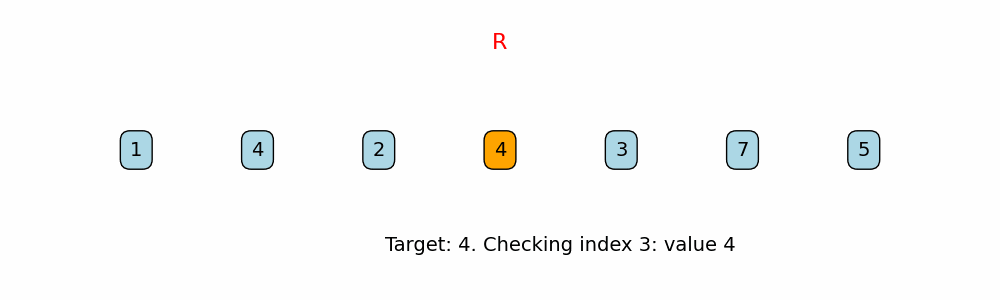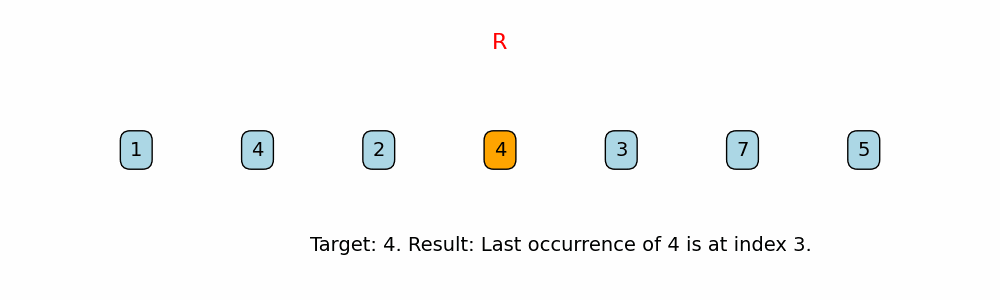
for i in range(len(nums) - 1, -1, -1):
if nums[i] == target:
return i
return -1
# Example usage:
nums = [1, 3, 5, 3, 2]
target = 3
result = find_last_occurrence(nums, target)
print("Last occurrence of", target, "is at index:", result)
-
Right-to-Left Traversal:
The function iterates over the array starting from the last index down to 0. This guarantees that the first time the target is found (when traversing from right to left) is its last occurrence in the array. -
Time Complexity:
The traversal takes O(n) time in the worst-case scenario (when the target is at the beginning of the array or not present), which meets the requirements.

No Comments