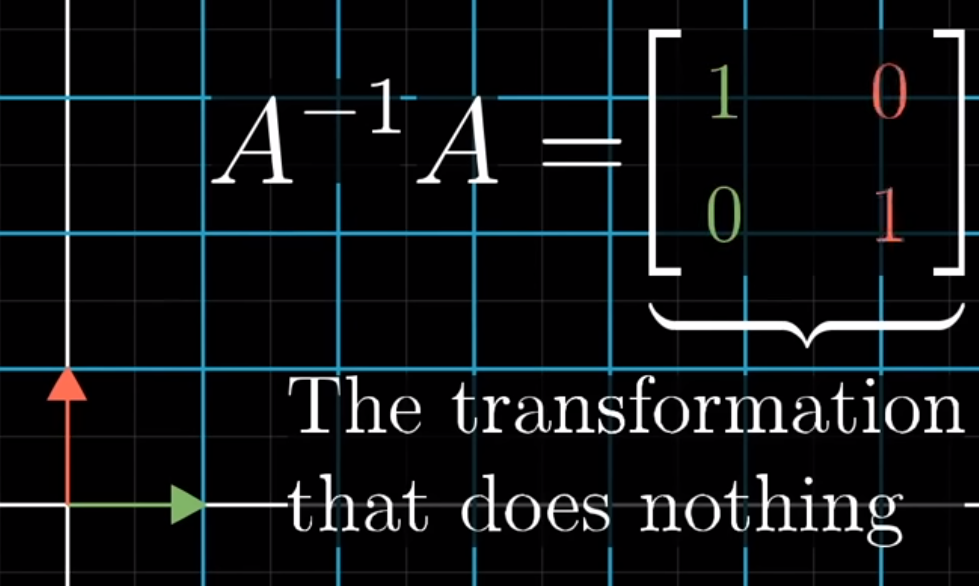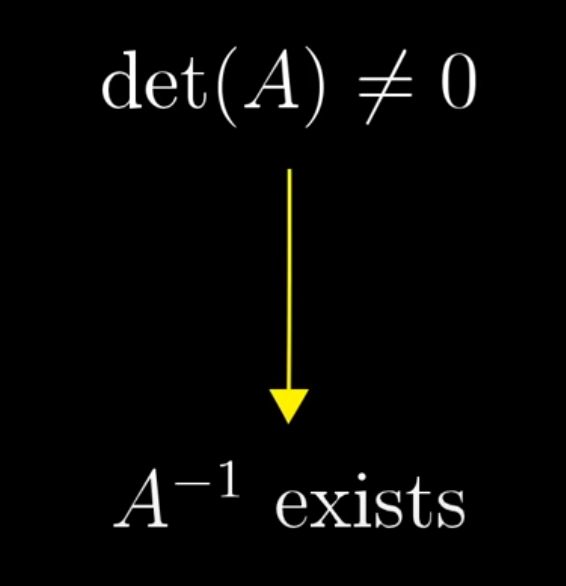Linear System of Equations
A system of equations consists of unknown variables and list of equations relating them.
A Linear System of Equations fulfill the following:
- The list of variable (xyz) is scaled by some constant number
- The only thing happening to each variable is that they are added to each other
- no exponents, no multiplication, no sin/cos/tan or other special functions
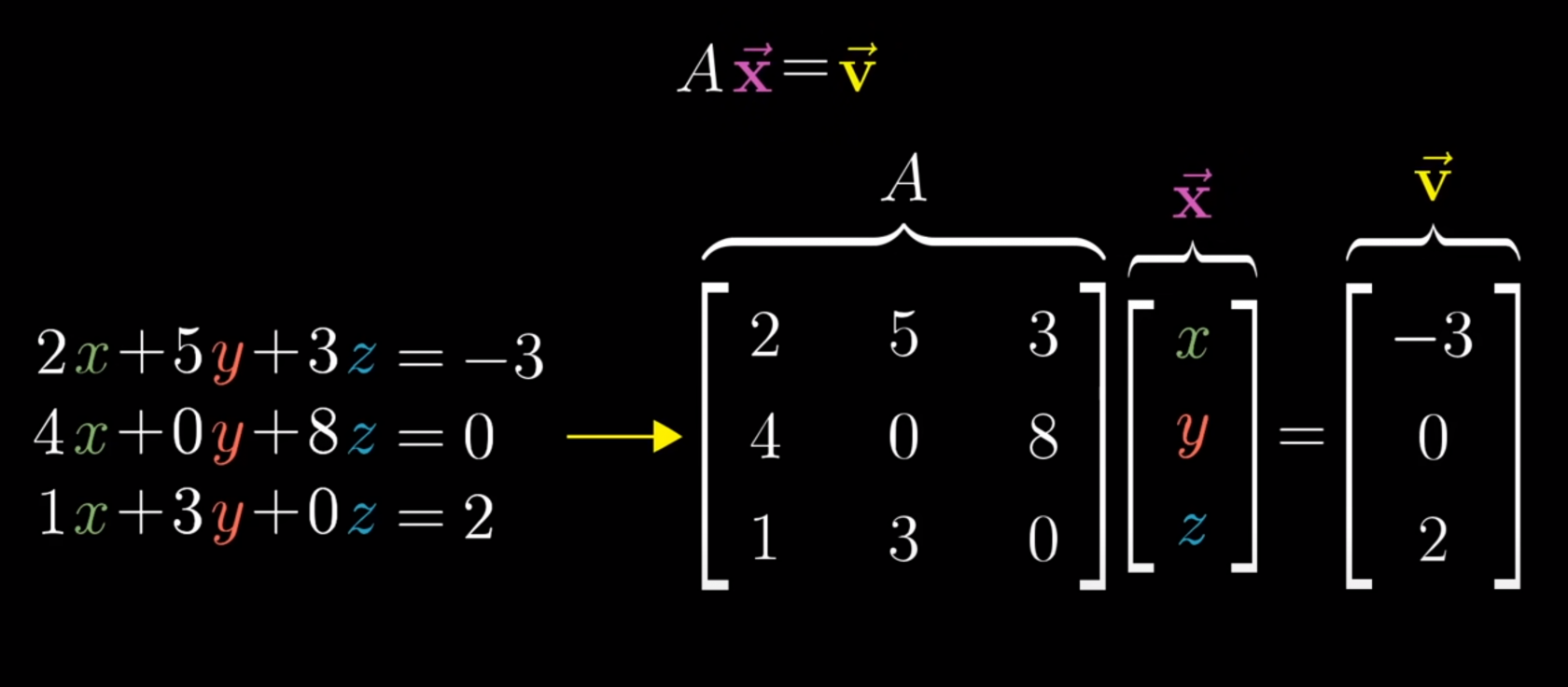
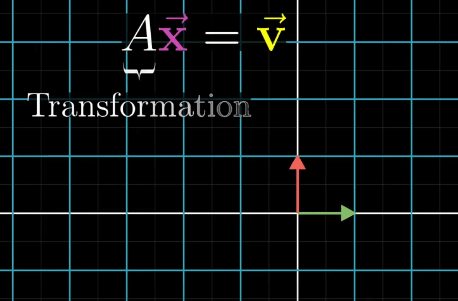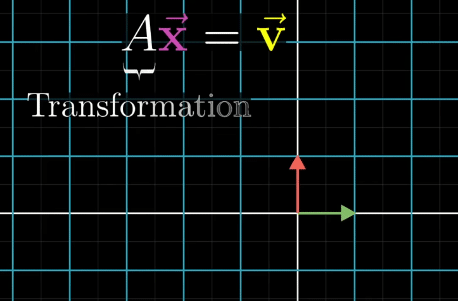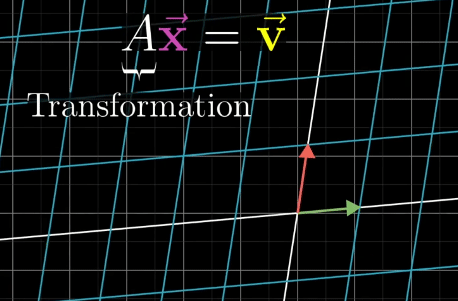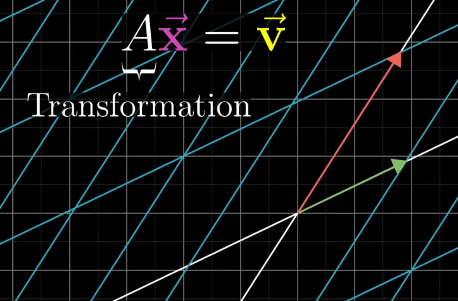
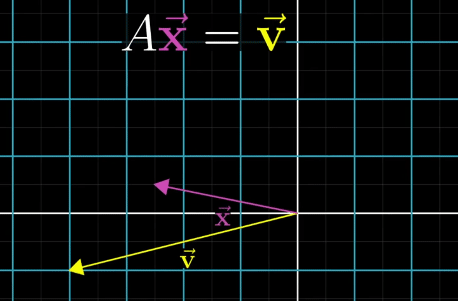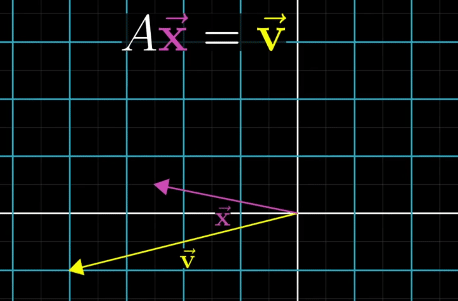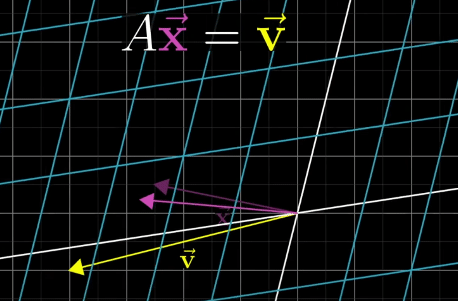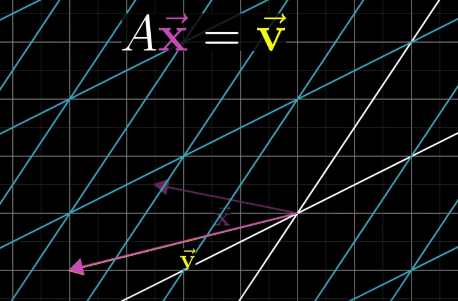
A Linear System of Equations is organized by putting scaled variables on the left and constants on the right. Also add Zeros to variables if not present.
A Linear System of Equations can be transferred to a vector equation with following equation, where A is the matrix holding all the constant coefficients.
ide
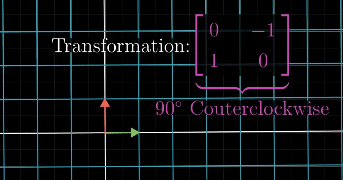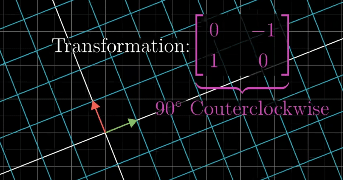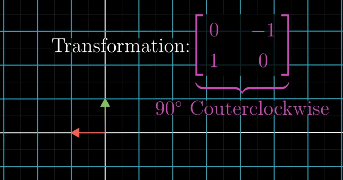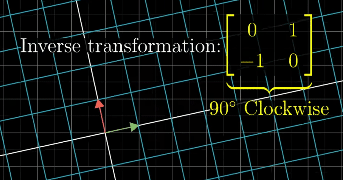
Inverse Transformation
Prereq: Determinant
identity matrix:
When determinant is 0, we can use Rank to describe the number of dimensions in the output of the transformation
Column Space
Null Space (Kernel)