Sliding Window: Dynamic
def dynamic_sliding_window(nums, target):
"""
Prints the steps of a dynamic sliding window algorithm.
Given an array of positive integers and a target sum, the algorithm finds
a contiguous subarray (window) whose sum is as close as possible to, but does not exceed, the target.
"""
print("Problem: Given an array of positive integers and a target sum,")
print("find a contiguous subarray whose sum is as close as possible to, but does not exceed, the target.")
print(f"Example: nums = {nums}, target = {target}")
print("-" * 70)
left = 0
current_sum = 0
# Start processing the array with a sliding window
for right in range(len(nums)):
current_sum += nums[right]
print(f"\nExpanding window: added nums[{right}] = {nums[right]}")
print(f"Current window (indices [{left} to {right}]): {nums[left:right+1]}")
print(f"Current sum: {current_sum}")
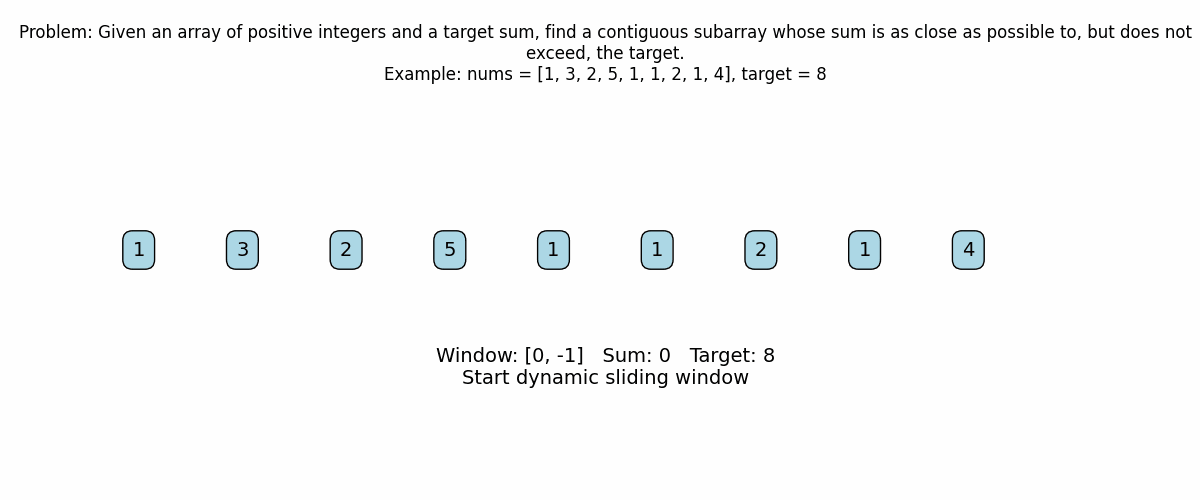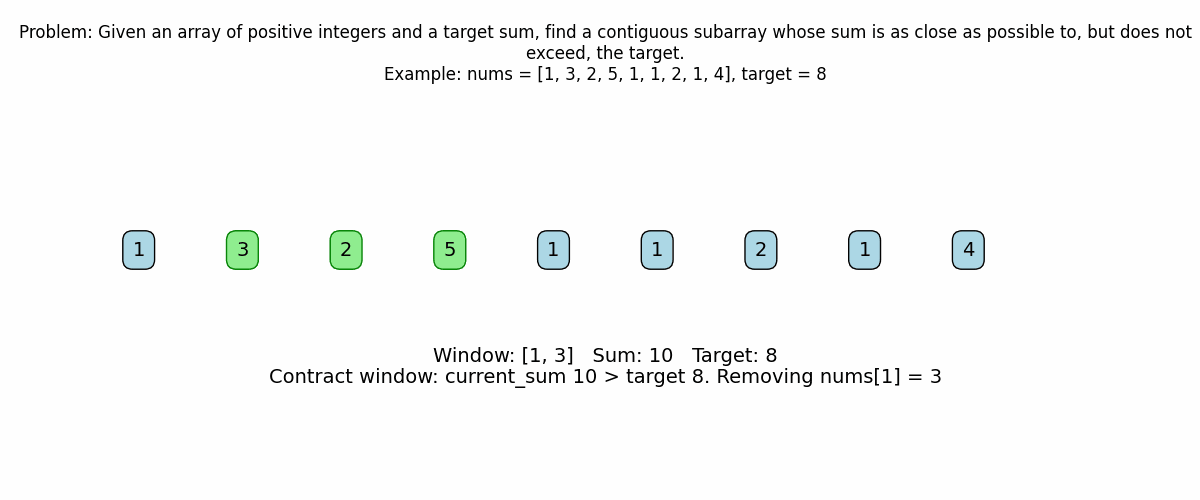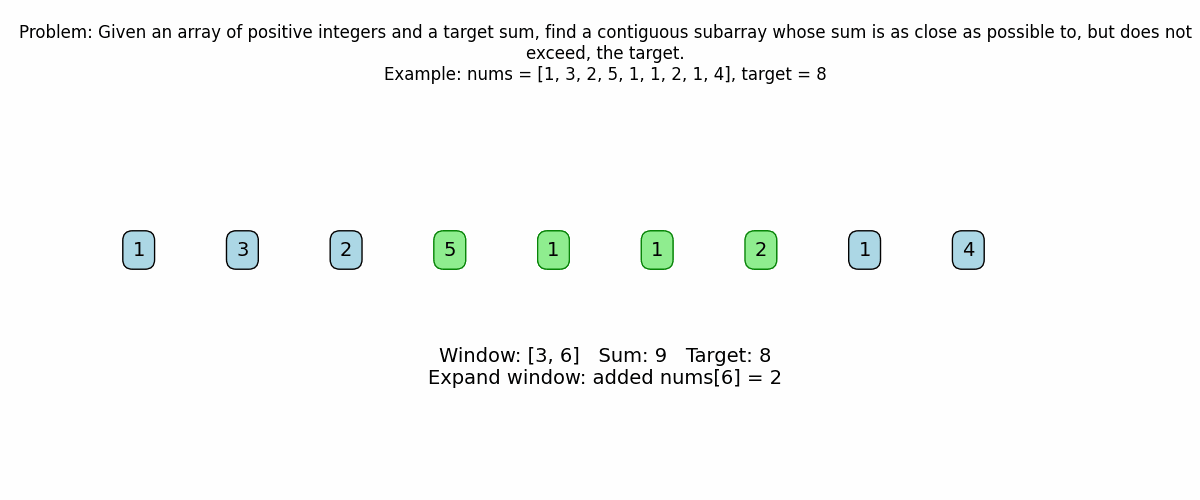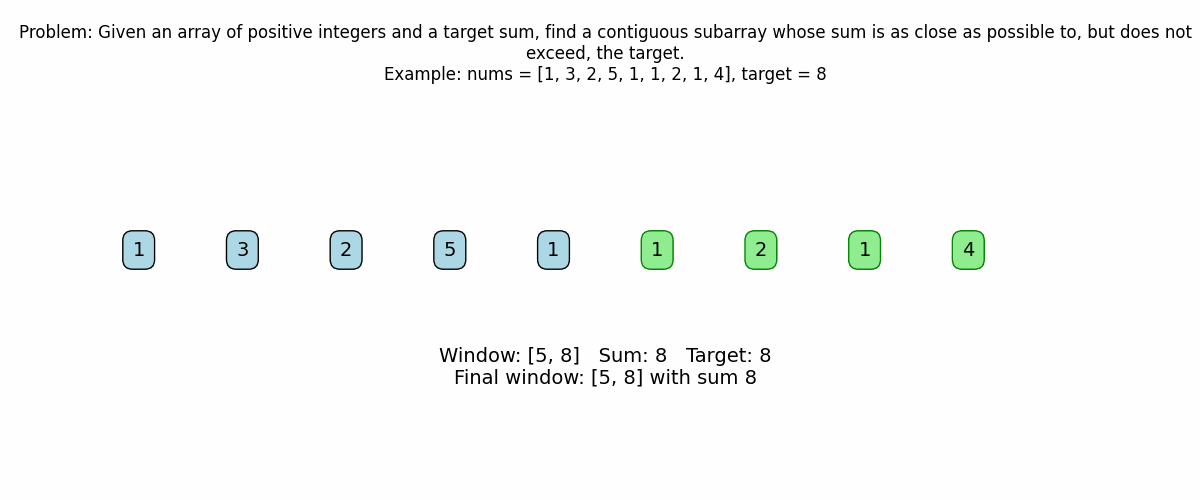
# Contract the window from the left if the current sum exceeds the target.
while current_sum > target and left <= right:
print(f" Sum {current_sum} exceeds target {target}. Removing nums[{left}] = {nums[left]}")
current_sum -= nums[left]
left += 1
print(f" After contraction, new window (indices [{left} to {right}]): {nums[left:right+1]}")
print(f" Current sum: {current_sum}")
print("-" * 70)
print(f"Final window (from index {left} to end): {nums[left:]}")
print(f"Final sum: {current_sum}")
# Example usage:
nums = [1, 3, 2, 5, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4]
target = 8
dynamic_sliding_window(nums, target)

